How many breadcrumbs are you leaving in the way of threat actors so that they can arrive directly and easily at your company?
According to statistics, 64% of companies worldwide have suffered at least one form of cyber-attack, and this trend seems likely to increase.
Indeed, more and more threat actors, i.e. those who intentionally cause harm in the digital world, conduct research manually or through the use of automated tools to find the best targets for their attacks. Malicious actors conduct detailed reconnaissance activities in order to carry out specific attacks that hit the chosen targets’ weak. No one can be considered safe from becoming a sitting duck, so more sophisticated defense strategies are needed now more than ever.
What is the Digital Footprint?
Digital Footprint is a service based on passive reconnaissance intelligence operation to identify a company’s attack surface. The analysis of the company’s external perimeter provides an overview of possible threats that an attacker can exploit for malicious purposes.
The external perimeter includes all the entry points, flaws and vulnerabilities through which attackers can attempt to gain unauthorized access to the company’s network, system, and data.
Other insidious threats that an attacker can exploit include cybersquatting and typosquatting – common techniques used to deceive internet users and gain access to sensitive information or spread malware. They work by creating fake websites that look like legitimate ones and are often based on common typing errors, such as misspelled domain names.

Cybersquatting and typosquatting
Specifically, cybersquatting is when an individual registers a website domain name which looks like that of a well-known brand or company in order to profit from the users’ confusion. Typosquatting is similar, but it involves registering a domain name that is the same as a popular website but has a typo in it (i.e. bipcybrsec.com. Can you notice the typo?)
These techniques are particularly dangerous for a company’s external perimeter because they can trick customers, partners, and employees into revealing sensitive information or unwillingly downloading malicious software.
The Digital Footprint can be useful in detecting and preventing these types of attacks. The service can also help the company monitor cybersquatting and typosquatting attempts and take action to prevent them before they cause harm. The BIP CyberSec Blue Team’ service assists companies in identifying their own digital footprint, which includes all online assets such as domain names, websites, and social media accounts.
Overall, the Digital Footprint is a crucial service for companies to protect their external perimeter and prevent cyber and typo squatting attacks that can lead to loss of reputation, financial losses, and other security risks.
1. The Methodology
The methodology developed to perform this service is based on manual researches conducted by the Blue Team Intelligence Specialists. The added value of the activity is in fact based not only on the collection of data and information, but on in-depth intelligence.
The Blue Team adopts the intelligence cycle, which consists of 7 phases:
- Planning & Direction: identification of the clients’ needs and development of a plan to address those needs.
- Collection: collection of information through various means and sources.
- Processing and Exploitation: in this stage, the information collected is reviewed and evaluated for relevance and reliability.
- Analysis and Production: the information is analyzed to produce a comprehensive report.
- Dissemination and Integration: the report is shared with the client and the results are discussed.
During the collection phase, ad-hoc tools are used to optimize the collection process, and only secure and trusted sources are selected to ensure reliable and accurate results. Once the intelligence cycle has been completed by the blue team specialists, the client is provided with a detailed view of the company’s critical issues and problems.
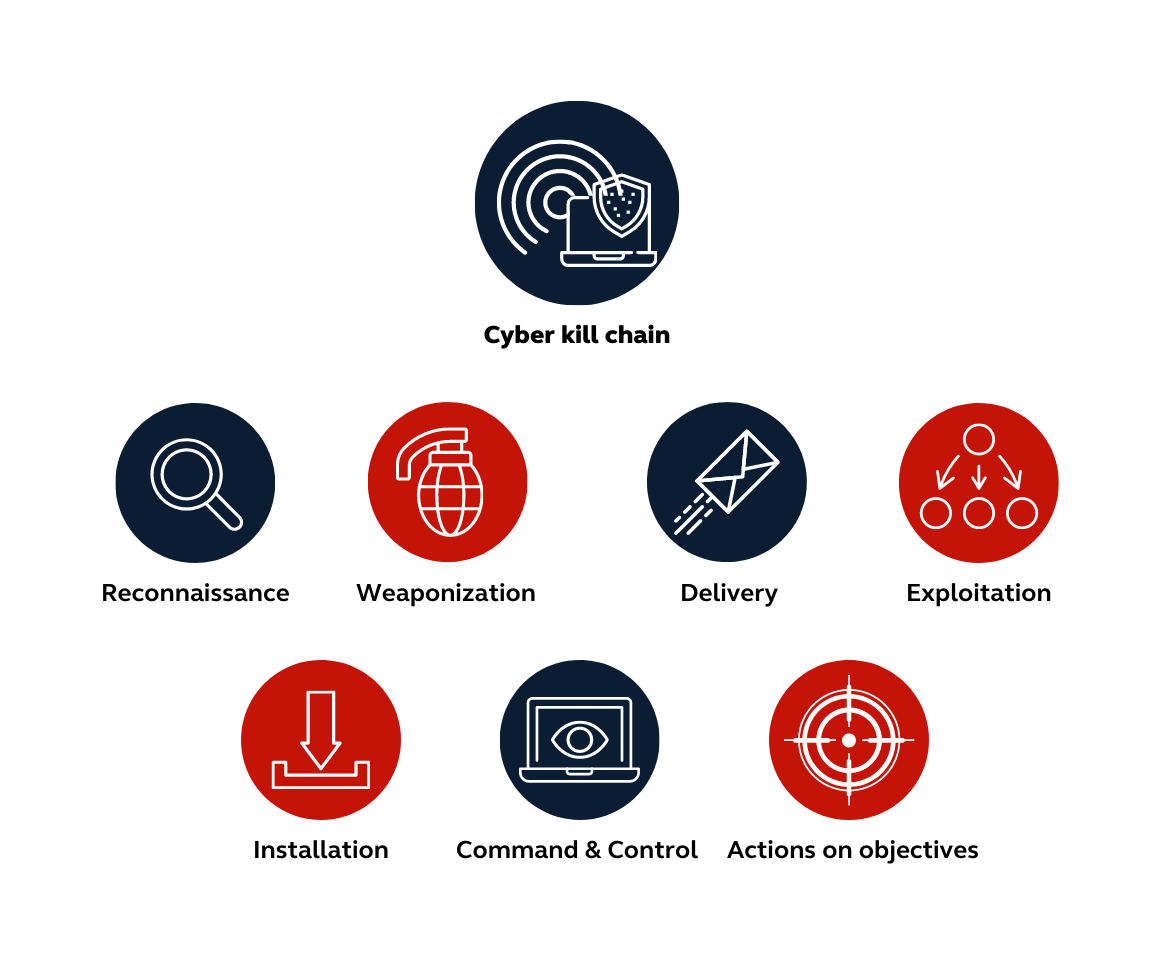
2. Reconnaissance phase – The Cyber Kill Chain
All attacks as we are taught by the Cyber Kill Chain & MITRE ATT&CK begin with reconnaissance activity.
Developed by Lockheed Martin in 2011 the cyber kill chain is a framework based on a military model that aims to define the main steps an attacker follows during an attack.
The Cyber Kill Chain is divided into seven stages:
- Reconnaissance: In this stage, the attacker gathers information about the target system, such as IP addresses, email addresses, and social media profiles.
- Weaponization: The attacker creates a malware payload, such as a virus or Trojan, and combines it with a delivery mechanism, such as an email attachment or a website.
- Delivery: The attacker delivers the malware to the target system, typically by tricking a user into downloading or executing it.
- Exploitation: The malware exploits a vulnerability in the target system to gain access and establish a foothold.
- Installation: The attacker installs additional tools and software on the compromised system to maintain persistence and evade detection.
- Command and Control: The attacker establishes a channel for communication with the compromised system and issues commands to carry out further actions.
- Actions on Objectives: The attacker achieves their goal such as, stealing sensitive data or disrupting operations.
By understanding the Cyber Kill Chain, defenders can develop strategies to detect and prevent attacks at each stage and disrupt the attacker’s progression towards their goal.
Reconnaissance is the starting point that the malicious actor uses to define which victims are most likely to be attacked and which target could guarantee a higher success rate. During the reconnaissance phase an attacker explores vulnerabilities and weaknesses that can be exploited within the network. A specific range of procedures and methods, including scanning, enumeration, and footprinting, are employed to gather and stealthily learn as much as possible about a target system.
Bip CyberSec Security Intelligence & Blue Team service is based on the use of passive reconnaissance, which aims to collect data on the target system without actively engaging with it. In active reconnaissance, on the other hand, during the data collection phases there is active engagement with the target system, for example by scanning ports to find which ones are open.
A peculiarity of passive reconnaissance is that it cannot be detected by commercially available monitoring systems, but it is still essential to know that someone is targeting your organization, as this is a major red flag.
Why is the Digital Footprint so important?
This activity is particularly helpful for:
- Defending the brand from possible threats and the spread of the related information
- Highlighting assets and domains that are part of shadow IT
- Analyzing the external perimeter
- Understanding what information an attacker can gather without any direct interaction with the target
- Identifying possible vulnerabilities, flaws and misconfiguration in a company’s digital infrastructure.
The overall output of the digital footprint activity allows the definition of specific scenarios, risk indicators and related remediation plans.
Stay one step ahead of cyber criminals with our advanced Digital Footprint service, which uses passive reconnaissance to identify vulnerabilities in your online presence and safeguard your information.